Nonlinear Least Squares fit¶
Overview¶
LGSL provides support for nonlinear least squares fitting for user-defined data and functions.
The problem of multidimensional nonlinear least-squares fitting requires the minimization of the squared residuals of \(n\) functions, \(f_i\), in \(p\) parameters, \(x_j\),
All algorithms proceed from an initial guess using the linearization,
where \(x\) is the initial point, \(p\) is the proposed step and \(J\) is the Jacobian matrix \(J_{ij} = df_i / dx_j\). Additional strategies are used to enlarge the region of convergence. These include requiring a decrease in the norm \(||F||\) on each step or using a trust region to avoid steps which fall outside the linear regime.
To perform a weighted least-squares fit of a nonlinear model \(Y(x,t)\) to data \((t_i, y_i)\) with independent Gaussian errors \(\sigma_i\), use function components of the following form
Note that the model parameters are denoted by \(x\) in this chapter since the non-linear least-squares algorithms are described geometrically (i.e. finding the minimum of a surface). The independent variable of any data to be fitted is denoted by \(t\).
With the definition above, the Jacobian is \(J_{ij} = \frac{1}{\sigma_i} d Y_i / d x_j\), where \(Y_i = Y(x,t_i)\).
Performing a non-linear fit¶
To perform a non-linear fit with LGSL, you should first define a function that computes the values \(f_i\) and \(J_{ij}\) for some given values of the parameters. The details about the function are given in the following section.
User defined function¶
The user-supplied function for the non-linear fit should calculate the values \(f_i\) and the elements of the Jacobian \(J_{ij}\) for a given set values of the parameters. The function is called with the following calling convention:
function fdf(x, f, J)
-- user defined function
...
end
where the function fdf is the function that you provide, x is column matrix that contains the \(p\) parameters, f is a column matrix of size \(n\) used to store the values \(f_i\) and J is a matrix of size \(N\) x \(P\) whose generic element \(J_{ij}\) is the derivative of \(f_i\) with respect of the \(j\)-th fit parameter.
In some cases the function can be called with f or J equal to nil because their values do not need to be computed. This implies that the user-defined function should always check the argument f and J and set their values only if the variable is not nil.
For example, let us suppose that we want to fit the function
where \(A\), \(\lambda\) and \(b\) are the fit parameters. Let us suppose also that we have sampled the data at \(n\) different values of \(t = t_1, \ldots, t_i, \ldots, t_n\). In this case, the vector x will have size \(p\), f size \(n\) and J size \(N\) x \(P\). The function for the non-linear fit can be therefore defined as follows:
function fdf(x, f, J)
for i=1, n do
local A, lambda, b = x[1], x[2], x[3]
local t, y, sig = i-1, yrf[i], sigrf
local e = math.exp(- lambda * t)
if f then f[i] = (A*e+b - y)/sig end
if J then
J:set(i, 1, e / sig)
J:set(i, 2, - t * A * e / sig)
J:set(i, 3, 1 / sig)
end
end
end
You can note in the definition above the we have chosen to store the three parameters \(A\), \(\lambda\) and \(b\) in this exact order. In general you should choose a certain order to pack the parameters into the vector x.
Note also that the assignment to the elements of the vector f and the matrix J are done only if their respective variables f and J are not nil.
Once the function is defined, the most delicate work is done and you should create a non-linear fit solver of the appropriate sizes \(n\) and \(p\) with the function nlinfit(). Once the non-linear fit solver is defined, you indicate the function fdf and the values using the method set(). Then you should iterate the search procedure with the method iterate() and test the convergence with the method test().
Here a complete example:
lgsl = require("lgsl")
-- number of data points
n = 40
-- sigma (error)
sigrf = 0.1
function fdf(x, f, J)
for i=1, n do
local A, lambda, b = x[1], x[2], x[3]
local t, y, sig = i-1, yrf[i], sigrf
local e = math.exp(- lambda * t)
if f then f[i] = (A*e+b - y)/sig end
if J then
J:set(i, 1, e / sig)
J:set(i, 2, - t * A * e / sig)
J:set(i, 3, 1 / sig)
end
end
end
function model(x, t)
local A, lambda, b = x[1], x[2], x[3]
return A * math.exp(- lambda * t) + b
end
xref = lgsl.matrix.vec {5, 0.1, 1}
r = lgsl.rng.new()
yrf = lgsl.matrix.new(n, 1, function(i) return model(xref, i-1) + lgsl.rnd.gaussian(r, 0.1) end)
s = lgsl.nlinfit {n= n, p= 3}
s:set(fdf, lgsl.matrix.vec {1, 0, 0})
print(s.x, s.chisq)
for i=1, 10 do
s:iterate()
print('ITER=', i, ': ', s.x, s.chisq)
if s:test(0, 1e-8) then break end
end
-- Plot the resulting fit alongside the simulated points (requires graph-toolkit)
graph = require("graph")
p = graph.plot('Non-linear fit example')
pts = graph.ipath(lgsl.iter.sequence(function(i) return i-1, yrf[i] end, n))
fitln = graph.fxline(function(t) return model(s.x, t) end, 0, n-1)
p:addline(pts, 'blue', {{'marker', size=5}})
p:addline(fitln)
p.clip = false
p.pad = true
p:show()
and here the resulting plot where we have superposed the simulated points with the best fit function.
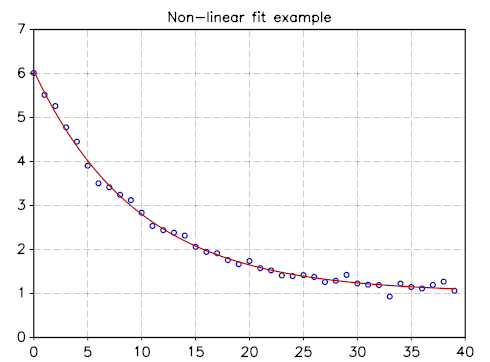
Non-linear fit of function A exp(a t) + b with Gaussian noise
Solver class definition¶
- nlinfit(spec)¶
Create a non-linear fit solver object. The argument spec should be a table of the form {n = ..., p = ...} where the fields n and p indicate` the number of observations and the number of fit parameters, respectively.
- class NLinFit¶
Non-linear fit solver class.
- set(fdf, x0)¶
Associate the non-linear fit solver with the user-defined function fdf and set the initial condition for the fit parameters to x0. The definition of the function fdf is given in the section above.
- iterate()¶
Advance the solver by a single step. It returns continue if it did not reach the optimal point and success otherwise.
- test(eps_abs, eps_err)¶
Check if the the search converged for the given absolute error eps_abs and relative error eps_rel.
- x¶
Returns the current vector with the fit parameters.
- f¶
Returns a vector with the fit residuals.